HELP FILE FOR GERARD'S RPN CALCULATOR

This help file displays and works best on a wide screen

This help file displays and works best on a wide screen
The image below shows the calculator with a label for each area for which you may need help.
Please click on the part of the calculator that you need help on or click here for an introduction to Reverse Polish Notaion (RPN).
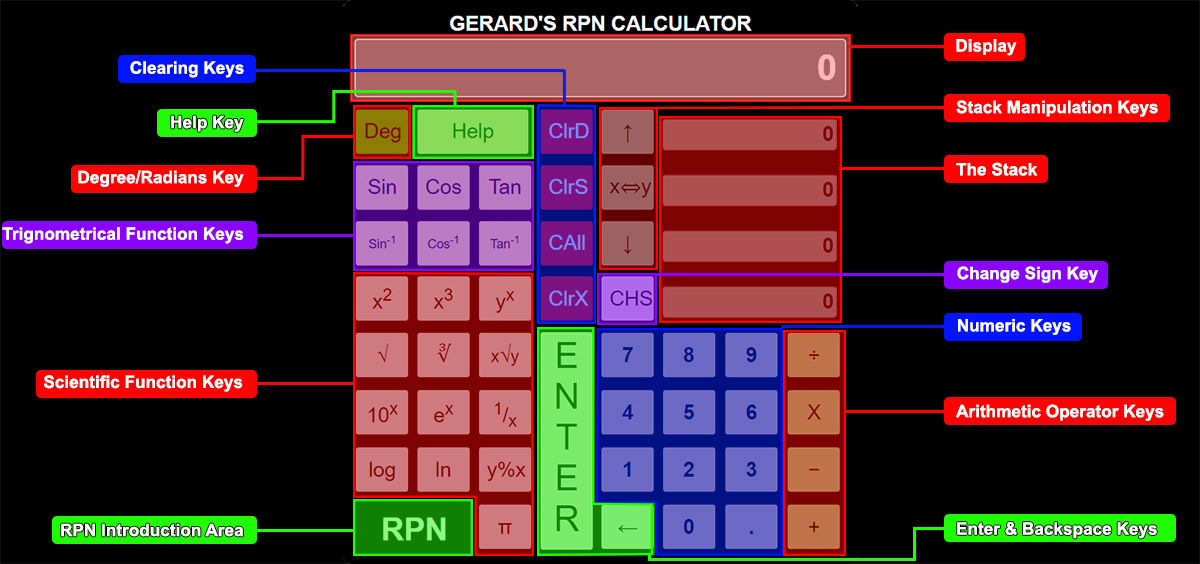


The display shows the results of any calulation done and is a reflection of the value in the bottom layer of the stack [𝑥 stack].
Error messages will also be display here.

The stack consists of 4 memory locations. HP calls them 𝑥, 𝑦, 𝑧 and 𝑡 from the bottom up. See image below.
Each time a number is entered the stack moves up and the entered number shows in the lowest stack (𝑥). Each of the other moves one up and that which was in the top (𝑡) is discarded.
Each time a calculation is done it uses the 𝑥 and 𝑦 (bottom two) or only the x (depending on the type of calculation) stack positions and places the result into the lowest stack position (𝑥) and the rest of the stack moves down.
When the stack moves down the top stack (𝑡) is copies down into 𝑧 and also retained in the 𝑡 stack.
This also provides an excellent way to do a calculation repeated with the same number. Just fill the stack with that number and it will always be available in the 𝑦, 𝑧, and 𝑡 locations.

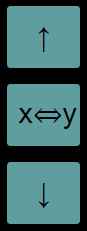 |
The Stack Manipulation Keys are used to move the contents of stack around. |
 |
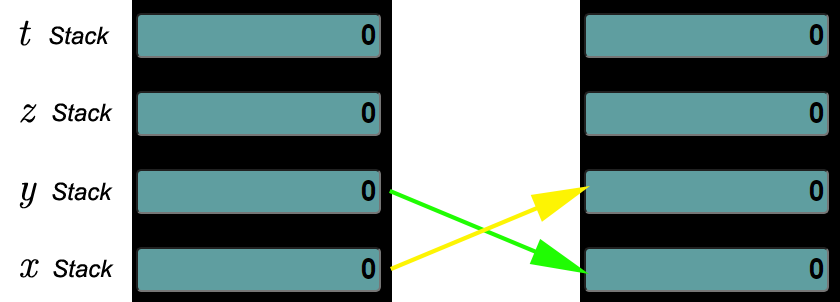
Rotates the stack up Value in 𝑥 moves to 𝑦 Value in 𝑦 moves to 𝑧 Value in 𝑧 moves to 𝑡 Value in 𝑡 moves to 𝑥 |
 |
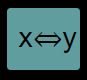 |
Exchanges the values of the 𝑥 and 𝑦 stacks |
 |
 |
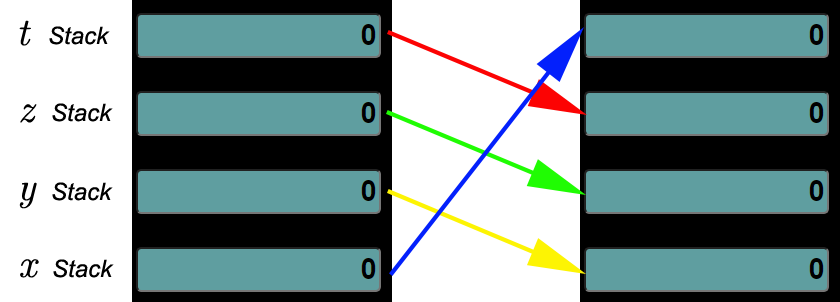
Rotates the stack down Value in 𝑥 moves to 𝑡 Value in 𝑦 moves to 𝑥 Value in 𝑧 moves to 𝑦 Value in 𝑡 moves to 𝑧 |
 |

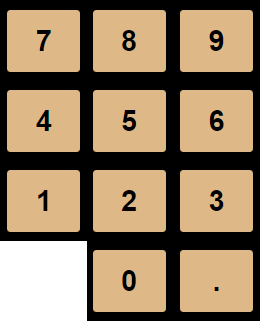
The numeric keys are used to type in the numbers which your want to do calcualtions with.
|
0 through 9 and . 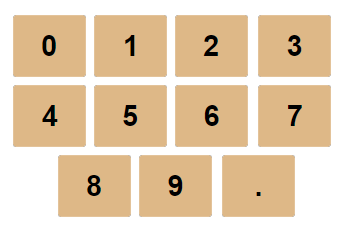
|
To input a value for calculation. The entry of a number ends when the Enter key is pushed or a function is executed. |

The Clearing Keys are used to clear values from specific memory locations.

 |
Clears the 𝑥 stack and the display. |
 |
Clear the stack, display and input. |
 |
Clears all the values in the stack (𝑥, 𝑦, 𝑧 and 𝑡). |
 |
Clears the display only. |


 |
Changes the sign of the value being entered or the value in the 𝑥 stack. |


 |
Terminates a value entry. |
 |
To delete the last numeric entry or the x stack if enter was pushed to terminate the entry. |

The Arithmetic Function Keys are used to execute arithmetic operations.
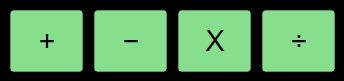
 |
Adds the value in the 𝑦 stack to that in the 𝑥 stack and places the answer in the 𝑥 stack and the display. |
 |
Subtracts the value in the 𝑦 stack from the value in 𝑥 stack and places the answer in the 𝑥 stack and the display. |
 |
Multiplies the value in the 𝑦 stack to that in the 𝑥 stack and places the answer in the 𝑥 stack and the display. |
 |
Divides the value in the 𝑥 stack into the value in the 𝑦 stack and places the answer in the 𝑥 stack and the display. |


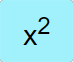 |
Takes the square of the value in the 𝑥 stack and places it back in the 𝑥 stack. |
 |
Takes the cube of the value in the 𝑥 stack and places it back in the 𝑥 stack. |
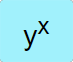 |
Raises the value in the 𝑥 stack by the power of the value in the 𝑦 stack and places the answer back in the 𝑥 stack. |
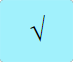 |
Takes the square root of the value in the 𝑥 stack and places it back in the 𝑥 stack. |
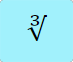 |
Takes the cubed root of the value in the 𝑥 stack and places it back in the 𝑥 stack. |
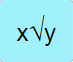 |
Takes the 𝑥 stack value’s root of the 𝑦 stack value and places it back in the 𝑥 stack. |
 |
Takes 10 raised to the value in the 𝑥 stack and places it back in the 𝑥 stack. |
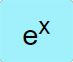 |
Takes ⅇ raised to the value in the 𝑥 stack and places it back in the 𝑥 stack. |
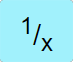 |
Takes the reciprocal of the value in the 𝑥 stack and places it back in the 𝑥 stack. |
 |
Takes the log base 10 of the value in the 𝑥 stack and places it back in the 𝑥 stack. |
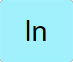 |
Takes the log base ⅇ (natural Log or ㏑) of the value in the 𝑥 stack and places it back in the 𝑥 stack. |
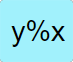 |
Takes the value in the 𝑦 stack as a percentage of the value in the 𝑥 stack and places it back in the 𝑥 stack. |
 |
Places the value of π in the 𝑥 stack. |

The Deg/Rad Key switches between degrees or radians when processing the trigonometrical functions.

 |
Deg displayed means the calculation will be done in degree mode. |
 |
Rad displayed means the calculation will be done in degree mode. |

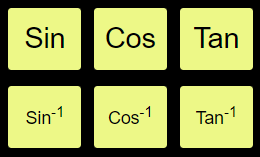
To learn more about these type of functions please follow the link below to Wikipedia
 |
Takes the Sine function of the value (deg or rad as per DEG/RAD indicator) in the 𝑥 stack and places the answer in the 𝑥 stack. |
 |
Takes the Cosine function of the value (deg or rad as per DEG/RAD indicator) in the 𝑥 stack and places the answer in the 𝑥 stack. |
 |
Takes the Tan function of the value (deg or rad as per DEG/RAD indicator) in the 𝑥 stack and places the answer in the 𝑥 stack. |
 |
Takes the Arcsine function of the value (deg or rad as per DEG/RAD indicator) in the 𝑥 stack and places the answer in the 𝑥 stack. |
 |
Takes the Arccos function of the value (deg or rad as per DEG/RAD indicator) in the 𝑥 stack and places the answer in the 𝑥 stack. |
 |
Takes the Arctan function of the value (deg or rad as per DEG/RAD indicator) in the 𝑥 stack and places the answer in the 𝑥 stack. |

The Help Key opens this help file.


This calculator is based on the operation of the HP 15c calculator that I have used for many years.
Below is a Image of the HP15c

Below is a Screen Shot of the Calacultor used on the web site

Reverse Polish Notion (RPN) is a way in which arithmetic calculations are described or done. Normally one is used to say “1 + 2 = 3”. The same sum in RPN would be said “1 enter 2 plus”. This is also referred to as “postfix” notation while the normal notation is referred to as “infix” notation.
There are many on-line resources explaining these notations and some are linked below for you to follow, if you so wish:
The principle is that the two numbers one wishes to use are entered first followed by the operation one wishes to execute on those two numbers. The numbers are placed in an “stack” and the answer is then inserted into the stack after removing the original two numbers.
On my calculator I have made the full stack visible and the bottom level of the stack (sometimes referred to the “𝑥” stack is also reflected in the display at the top of the calculator. (On the HP15c only the bottom of the stack [𝑥 stack] is seen on the display at all times).
To learn more about the stack click on the button below

Works best on a Computer or screen wider than 690px
Click here to go back to the Technical Index Page